The Hidden Dangers of Artificial Intelligence in Business
The Hidden Dangers of Artificial Intelligence in Business

Artificial intelligence (AI) is becoming an indispensable tool in the business world, offering greater efficiency, automation of repetitive tasks, and data analysis with exceptional accuracy and speed. However, it is crucial to consider the potential dangers that it can bring carefully. Behind these promises of high productivity lie potentially devastating risks that threaten to disrupt the balance of any business. From security flaws and algorithmic biases to increased technological dependency, the intensive use of AI could be a potentially sharp weapon. This article explores the underestimated dangers of this technological revolution in business.
Privacy and Security Risks
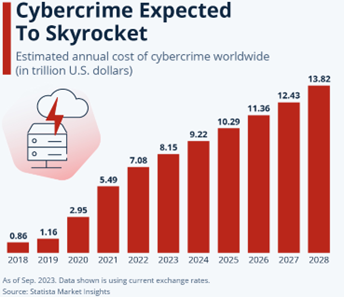
AI processes massive amounts of data to make informed decisions, which raises significant concerns about data privacy and security. Without adequate security measures, sensitive data from customers, patients, or businesses can be compromised. For instance, AI can analyze medical records to propose diagnoses in the medical field. However, if these systems aren’t adequately secured, patients’ confidential information could be exposed to cyberattacks, resulting in privacy breaches and data loss.
Moreover, businesses using AI to manage financial information must be particularly vigilant. AI algorithms can be targeted by hackers seeking access to critical financial data, leading to disastrous consequences. The complexity and interconnectivity of AI systems often make it difficult to identify and fix vulnerabilities, increasing the risk of data breaches. Once a vulnerability has been exploited, it can be extremely difficult to remediate the damage caused.
Technological dependency and loss of skills
Over-automation can lead to an over-reliance on AI, where human skills are pushed aside, creating a potential vulnerability. As companies integrate more and more AI into their operations, this can lead to a deterioration of essential human skills, such as problem-solving, decision making, and creativity. Employees can become overly dependent on the recommendations of Artificial Intelligence systems, neglecting their judgment and expertise.
This loss of skills can leave businesses vulnerable to technological failure. Businesses need to maintain the balance between Artificial Intelligence and human expertise, recognizing that AI is a tool to help, but cannot completely replace human intelligence. Complex situations and strategic decisions often require nuance and judgment that Artificial Intelligence cannot provide. What’s more, if Artificial Intelligence fails, companies that have relied too heavily on these systems may find themselves helpless, unable to function effectively without their assistance.
In an interview with WUNC, Microsoft CEO Satya Nadella, discussed the promises and potential dangers of AI. He underlined the importance of keeping humans at the center of AI systems to avoid mistakes and misunderstandings: “We decided to design this as a co-pilot, not an autopilot. The human must remain in control.” – WUNC
Biais and Discrimination
Artificial Intelligence systems are only as good as the data they are trained on. However, this data can contain implicit biases, leading to discriminatory decisions. But what exactly does this mean? Bias in the context of AI refers to a systematic tendency to favor certain outcomes or groups of people over others, often unfairly or inequitably. These biases can be introduced at different stages in the development of Artificial Intelligence.
For example, Artificial Intelligence can reproduce and amplify existing biases in an algorithm’s training data, leading to unfair or discriminatory results. A customer service bot trained on biased data where certain customer questions are systematically neglected can replicate this neglect, delivering a negative and unequal customer experience. Biases in Artificial Intelligence can also manifest themselves in recruitment systems, where algorithms favour certain demographic groups over others, perpetuating existing inequalities.
For companies, biases in Artificial Intelligence systems can cause reputational damage, legal risks, and economic damage… leading to public criticism and loss of customer confidence. Companies must therefore be vigilant in the design and deployment of their AI systems, putting in place mechanisms to identify and correct potential biases. This can include regular audits of Artificial Intelligence systems, diversification of training data, and the involvement of various stakeholders in the development process. By taking these steps, companies can minimize the risk of bias and ensure that their AI systems operate fairly and responsibly.
"She declined to say how many employees were working on racial bias, or how much money the company had allocated toward the problem."
— @timnitGebru@dair-community.social on Mastodon (@timnitGebru) July 5, 2023
Simple question: what percentage of your humanity saving workforce is Black? For OpenAI, I bet it can be rounded to ZERO.https://t.co/IXyy7zWDvZ
Risk of misinformation and manipulation
AI systems can be exploited to disseminate false information on a large scale and manipulate public opinion, posing a considerable danger to society and democracy. A notorious example is the use of advanced language models such as ChatGPT to generate fake content or Deepfakes to create fake videos that can falsely represent real people. These technologies can be used to influence political opinions and cause conflict.
AI’s ability to manipulate raises significant ethical and regulatory challenges. Companies developing and deploying these technologies need to be aware of the potential implications and take steps to prevent their misuse. Increased regulation and accountability in the use of AI for communication and influence is essential to prevent misuse and protect society. Without proper control, AI can become a powerful tool for misinformation.
AI Failure and Accountability
AI systems are playing a central role in various industries, from healthcare to finance to transport. However, their complexity and dependence on data and algorithms make them vulnerable to error. The failure of an Artificial Intelligence system can have disastrous, sometimes catastrophic consequences. For example, a defective medical diagnosis algorithm may recommend inappropriate treatment, putting patients’ lives at risk. Similarly, a failure in an automated driving system could lead to accidents, resulting in injury or death.
The question of responsibility in the case of failure of Artificial Intelligence is particularly complex. Who is liable if Artificial Intelligence fails? The software developer, the company that deployed it, or the end user? This legal ambiguity highlights the need to develop clear and precise regulatory guidelines for accountability in the case of AI failure. Legislators need to work with technology experts, companies and users to define rules and standards that clarify responsibility and protect all parties involved.
To minimize the risk of default and clarify liability, companies need to adopt a proactive approach:
- Rigorous Testing: Implement thorough testing processes to identify and correct bugs and errors before deployment.
- Continuous Monitoring: Use monitoring tools to detect anomalies and potential failures in real-time.
- User Training: Train end users to ensure they understand how to use the system correctly and interpret its results.
- Contractual Clauses: Include clear clauses in contracts regarding liability in case of failure, defining each party’s obligations.
The integration of AI into businesses offers immense opportunities to improve efficiency and productivity. However, the associated risks mustn’t be disregarded. To successfully navigate in this technological era, it is essential to put in place robust safety measures and strict regulations, to maintain a balance between Artificial Intelligence and human expertise, and to promote the ethical and responsible use of these technologies. In this way, businesses can make the most of AI while minimizing the potential dangers. In addition, it is essential to focus on cybersecurity innovations to protect sensitive data and prevent cyber attacks, while continuing to explore the potential of AI in various sectors such as healthcare, education, and finance.



